This article explores what is the relation between EU CAP inspections and GNSS, the GNSS specifications for it and why the Leica Zeno FLX100 smart antenna can be used throughout Europe for CAP inspections.
What are EU CAP inspections?
The European Union Common Agricultural Policy (EU CAP) is a set of regulations that includes payment of subsidies to farmers under various schemes. Each member state must carry out a number of farm inspections each year to check:
- Information provided by subsidy claimants is correct.
- Legal and administrative regulations are being correctly followed.
Amongst other factors, subsidies are paid out based on the area of land used for appropriate farming practices. It is important that area information submitted by a claimant is correct. During inspections, land parcels and other features are measured by paying agencies using GNSS equipment. For this purpose, the equipment must be certified and approved by the Joint Research Centre (JRC) of the European Commission.What are the requirements for successful certification?
The JRC stipulates that GNSS equipment must have a buffer width of no more than 1.25m (class 2) and recommends no more than 0.75m (class 4). The following test procedure is used to prove a smart antenna is accurate enough for EU CAP inspections:
- Six land parcels between 0.2 hectares and 1.8 hectares and of different shapes are marked on the ground.
- Each parcel is measured a total of 36 times.
- Nine rounds for each parcel are completed in 4 different runs to reproduce typical conditions in the real world, such as different times of the day and walking direction.
- The 36 areas are computed and analysed for each parcel which results in the average buffer width.
New Smart Antenna, new certification
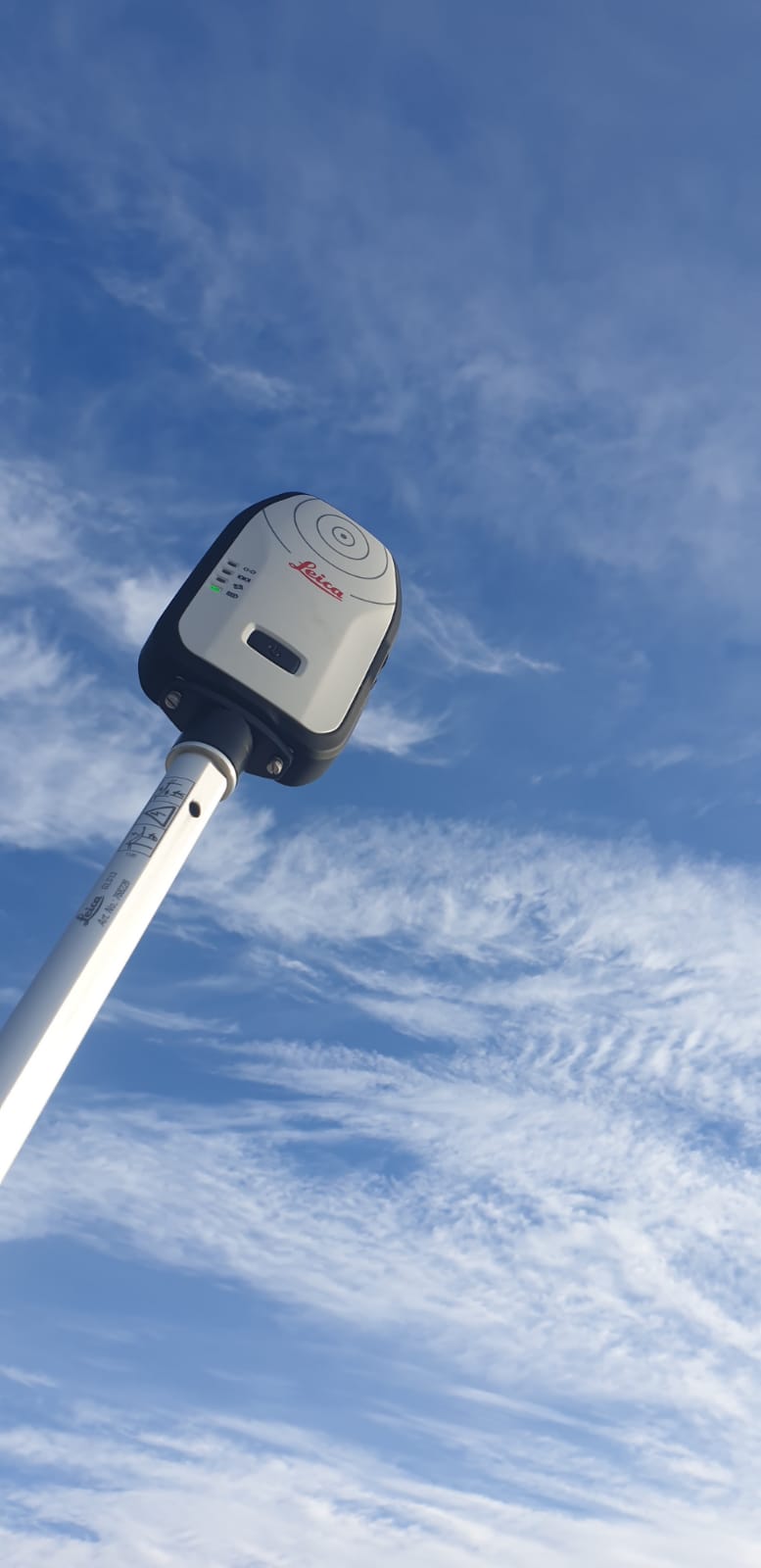 The Leica Zeno FLX100 smart antenna is a new, a multifrequency survey-grade GNSS device that can be used with Leica Zeno Mobile or Zeno Connect software. As with all new Zeno smart antennas, to gain JRC certification the Leica Zeno FLX100 was put through its paces at the Leica Geosystems testing laboratory near the headquarters in Switzerland.
The Leica Zeno FLX100 smart antenna is a new, a multifrequency survey-grade GNSS device that can be used with Leica Zeno Mobile or Zeno Connect software. As with all new Zeno smart antennas, to gain JRC certification the Leica Zeno FLX100 was put through its paces at the Leica Geosystems testing laboratory near the headquarters in Switzerland.
Let’s have a look at how the certification test was carried out.
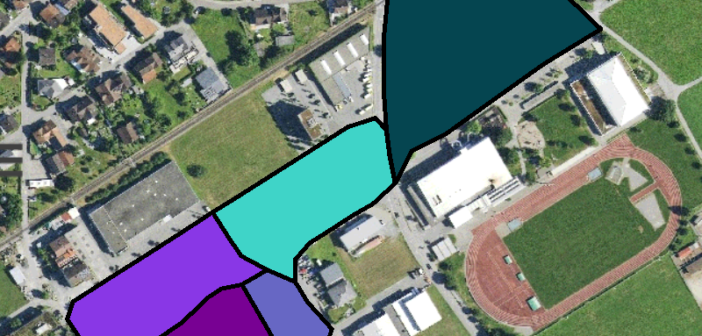
The test site
As previously mentioned, the test site is made up of six land parcels is in a semi-urban environment with a mixture of buildings, trees and open sky. It is important there is a variety of terrain and obstacles on the test site to reproduce as close as possible conditions inspectors would face when visiting farms.
Hardware
The Leica Zeno FLX100 was paired with the Leica Zeno Tab 2 Android tablet. The test was done in mid-December and the weather conditions included snow and ice, so it was important a rugged and weatherproof mobile device was used.
Software
The easy to use Leica Zeno Mobile app was used to collect the GNSS data. The reference parcel data was imported into a Zeno Mobile project and the layers used to store the GNSS measurements were prepared in the Zeno Data Model for Excel spreadsheet. This is a very useful tool that allows a data model to be prepared in advance and imported into Zeno Mobile ready for data collection.
Services
A network RTK connection using a local Leica Spider network was used to gain centimetre accurate measurements with the Leica Zeno FLX100. The Zeno Tab 2 used a mobile SIM card to access the internet and enable connection to the RTK network.
Points, points and more points
 After setting up the equipment, Simona Hriscu, a Product Engineer in Leica Zeno team, carried out the measurements at the test site.
After setting up the equipment, Simona Hriscu, a Product Engineer in Leica Zeno team, carried out the measurements at the test site.
Over the course of nine days, an enormous 5,000 GNSS points were measured. Each day was a full eight hours of measuring covering around 20km on foot, so it was not only an endurance test for the surveyor, but also for the equipment.
Both the Leica Zeno FLX100 and Zeno Tab 2 had more than enough battery life for a full day’s work. The GNSS measurements were synchronised with Esri ArcGIS Online to backup the data and to simplify the Q/A process at the end of each day.
The final result
Once the data collection was complete, all the GNSS measurements were run through statistical tests to compute the average buffer width.
The final result was 0.02m ±0.01m which corresponds to the best class 5 < 0.50m that can be awarded for certification. Now the Leica Zeno FLX100 smart antenna can be used throughout Europe for CAP inspections!
Learn more about the Leica ZenoFLX100 smart antenna.

Senior Product Engineer at Leica Geosystems