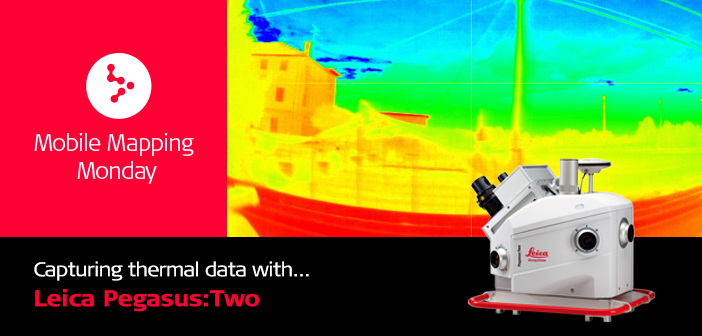
Beside LiDAR data and images the Leica Pegasus:Two mobile mapping solution is designed to host additional sensors such as GPR (Ground Penetration Radar) and thermal cameras. By adding additional dimensions to our geospatial data layers, users have a complete picture of the environment, providing critical support to any decision processes for their clients.
A thermal camera offers information hidden to our eyes. It supports proactive infrastructure maintenance and gives professional control over diagnostics.
As more and more people realise the great potential of this imaging technology, thermal cameras are used today in many applications and in a variety of ways:
Detecting Leaks
The thermal sensor hosted on the Pegasus:Two can assist in diagnosing and detecting leaks. It allows professionals to locate leaks where there is no physical evidence of any water damage. Cracks that develop from contraction of concrete during curing, inappropriate material selection, and the structure’s inability to accommodate movements due to thermal changes are the most common cause of leakage.
Leaks on underground structures such as highways and rail tunnels can result in erosion and, ultimately, affecting public safety. Getting these issues georeferenced is the key for maintenance – knowing where to look. The thermal imaging delivers precious information to engineers for highway and rail tunnels projects. It enables them to calculate and establish recommended leakage rates based on international standards and experiences.
Monitoring Overheating Transformers
Transformer fluid leaks cause overheating that leads to failures. A failure can cause black-out of power to a whole area and can even be very dangerous. Used as a condition-monitoring technique the Leica Pegasus:Two allows users to capture and georeference overheating transformers by using the thermal camera. The camera is sensitive enough to detect a temperature raise. It provides timely information on the health status of the power network, prevents power outages and thus contributes to cost efficiency.
Inspecting Power Lines
It’s essential for utility companies to do preventive maintenance assessments to provide customers with uninterruptible power supply. When used with a thermal camera, the Leica Pegasus:Two delivers a cost-effective solution for surveying many kilometres of power lines.
When residential areas are analysed to identify any thermal dispersion, thermal cameras support the inspection even when the object is hidden from the LiDAR technology. By navigating through thermal images, power lines are clearly highlighted even when hidden under dense vegetation. With a complete power line map the accuracy of deliverables is higher.
Courtesy of ETS, Italy
The effective use of thermal imaging creates real savings in reduced work hours. When fully and effectively deployed with the Leica Pegasus:Two, it reduces outages and man hours and improves process control and operational efficiency.